
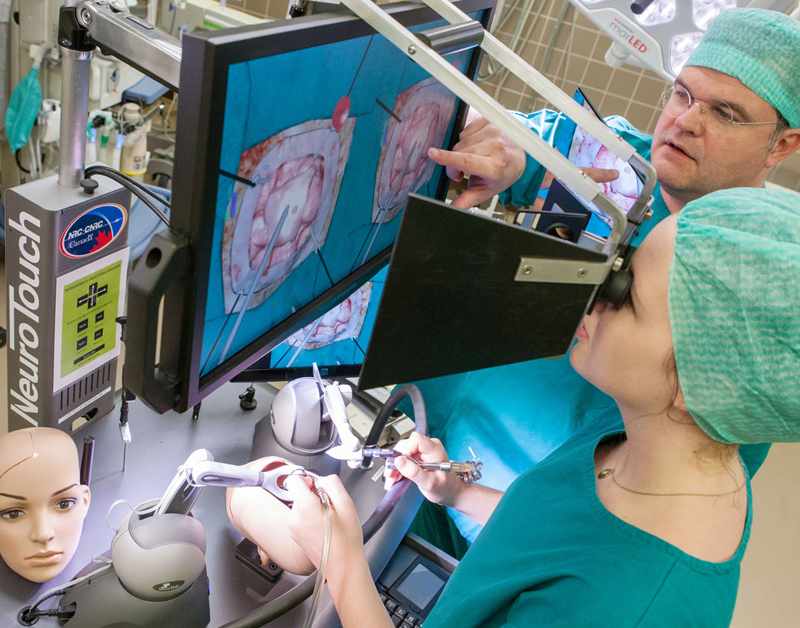
Modern surgical skills training now mostly relies on hands-on simulation since it provides a realistic and safe setting for practicing surgeons, medical students, and residents to improve their methods. Simulation-based training lets students actively interact with surgical equipment, anatomical models, and virtual reality systems rather than depending just on observation and restricted real-patient exposure as in conventional learning approaches. All of these are absolutely essential for surgical excellence; this immersive experience improves muscle memory, decision-making, and confidence.
High-fidelity simulators accurately replicate real-life situations. This lets trainees practice tough operations repeatedly. They can do this safely, without risking patients. Simulation builds skills through practice and feedback, whether in laparoscopic surgery, suturing, or emergency care.
Furthermore, practical simulation promotes a competency-based learning approach by letting teachers evaluate abilities impartially and customize teaching to fit particular requirements. It closes the theory-practice gap and gets surgeons ready for exact and efficient performance in actual operating rooms.



















Write a comment ...